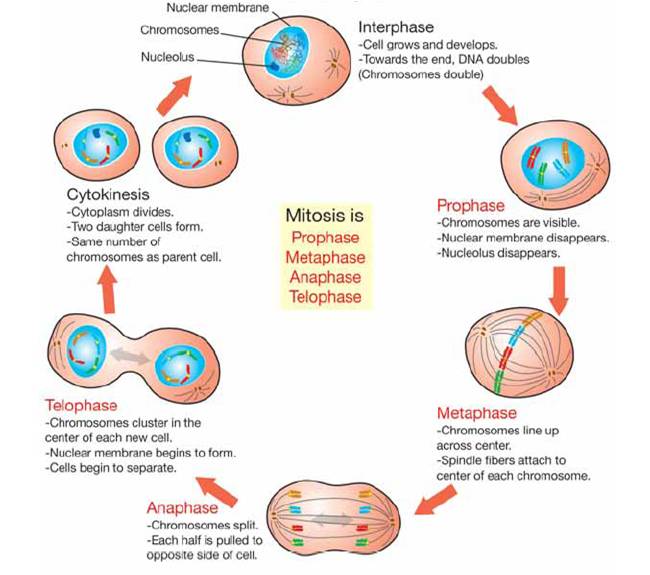
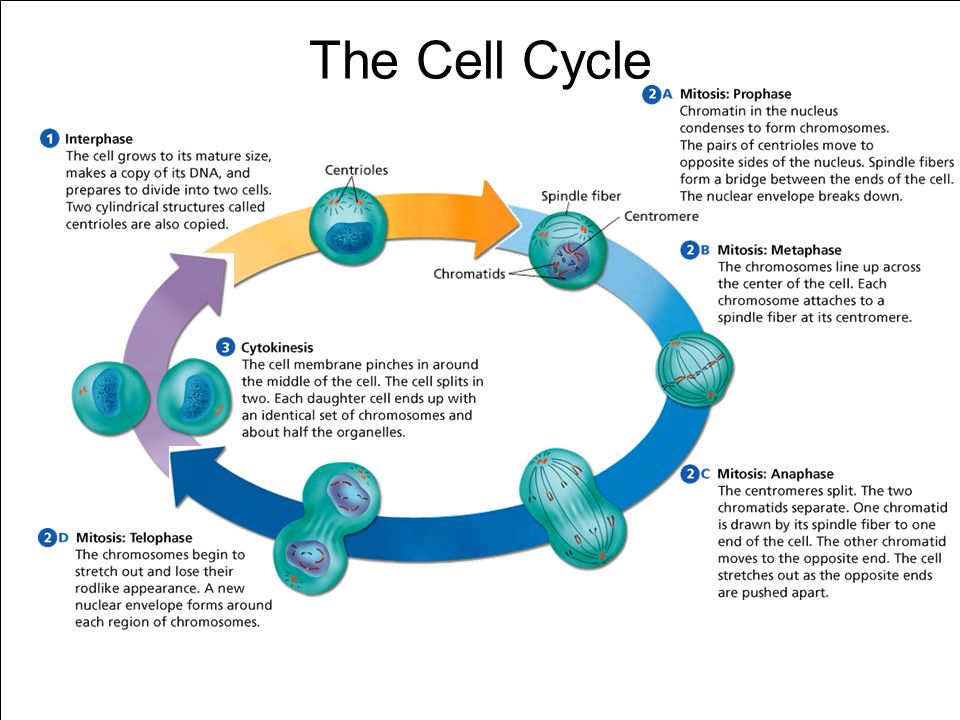
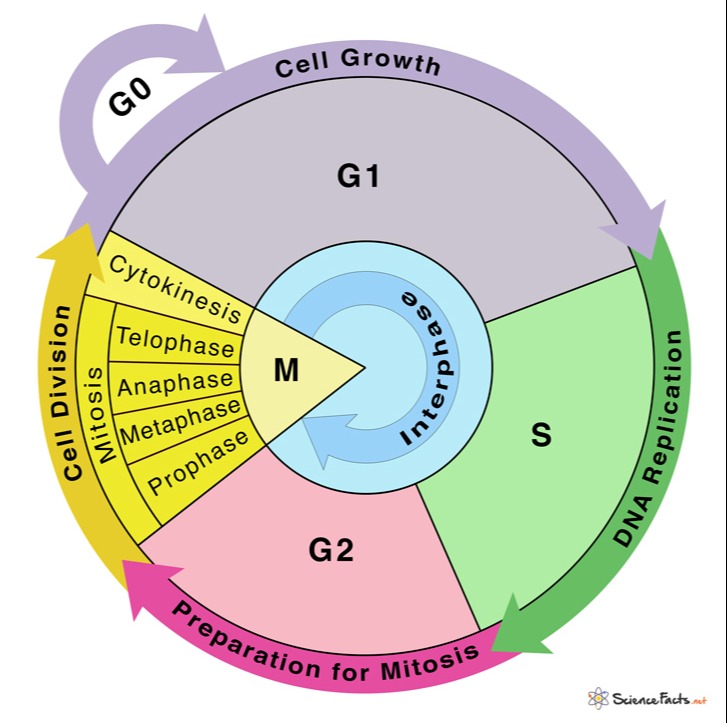
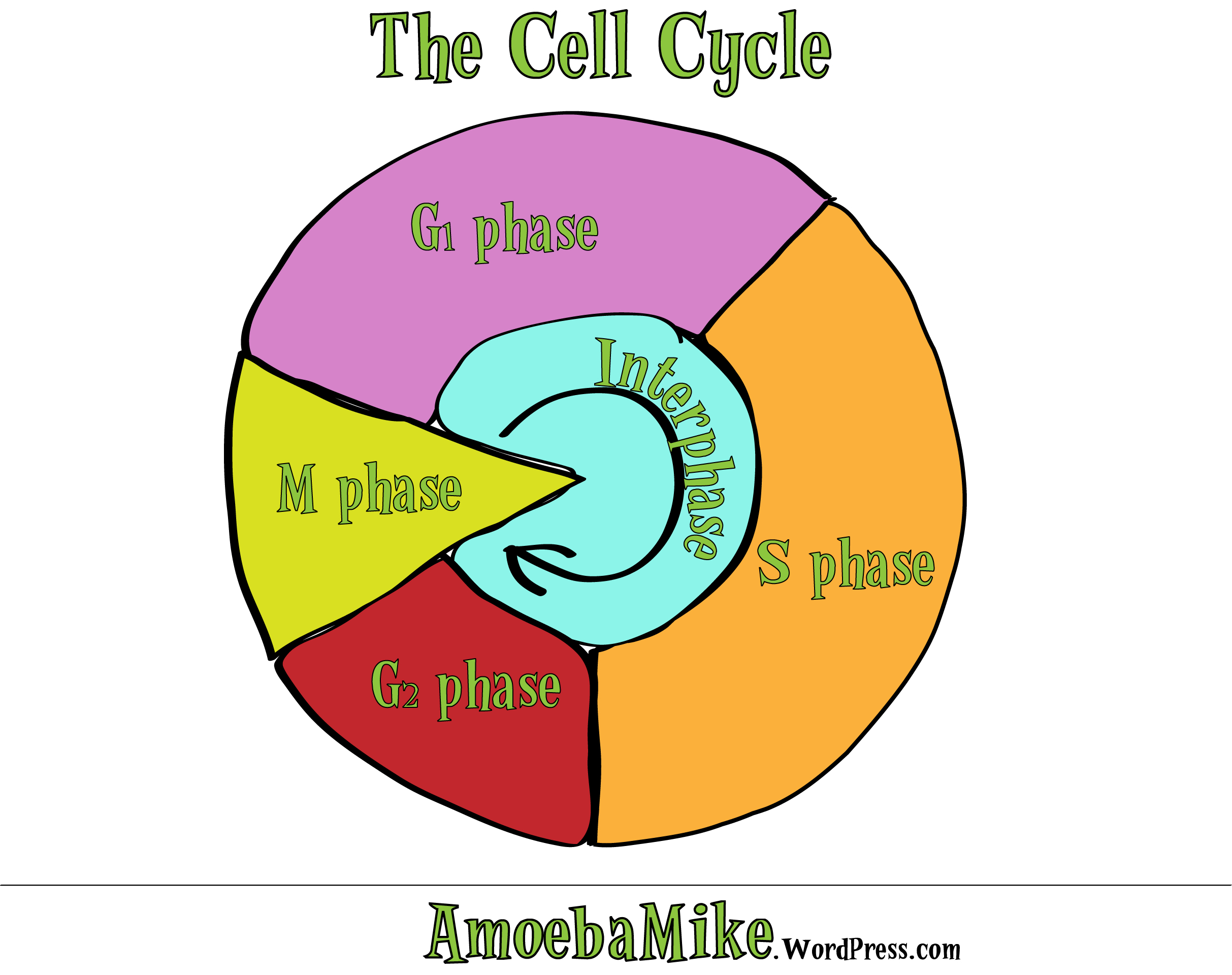
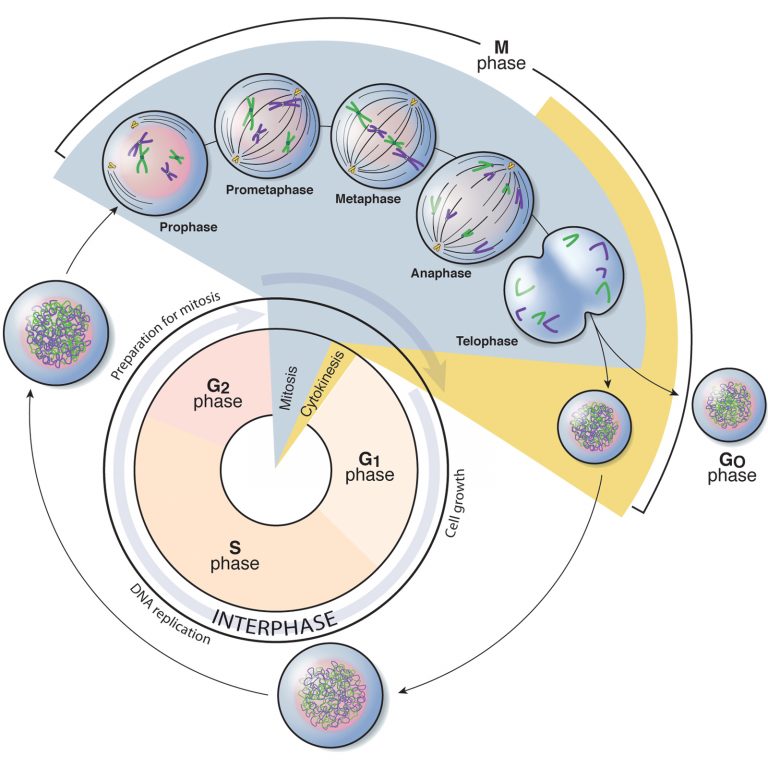
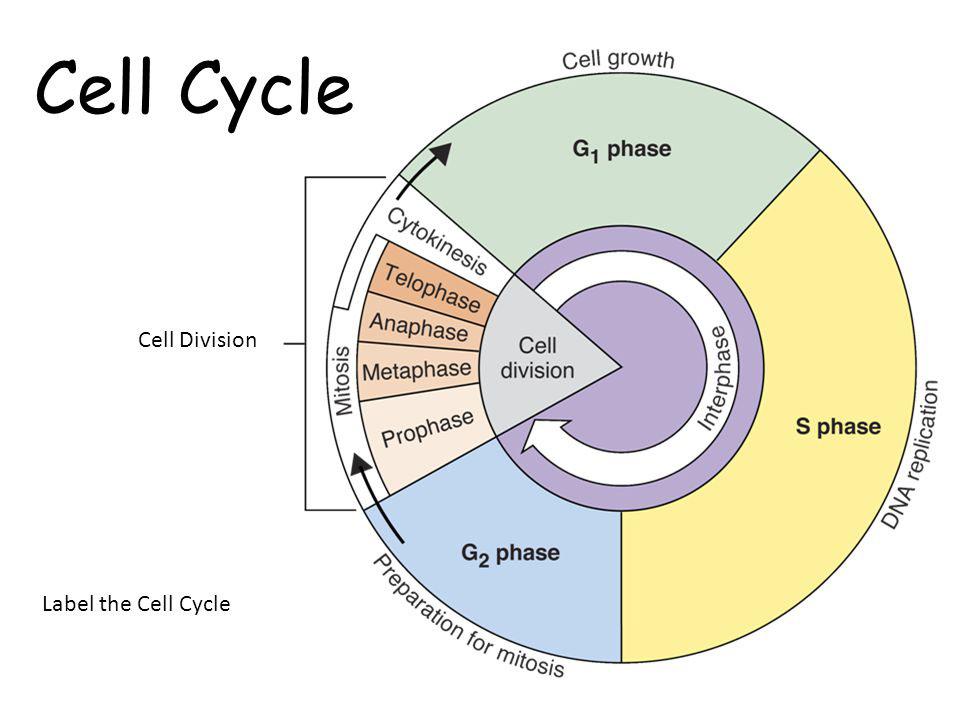
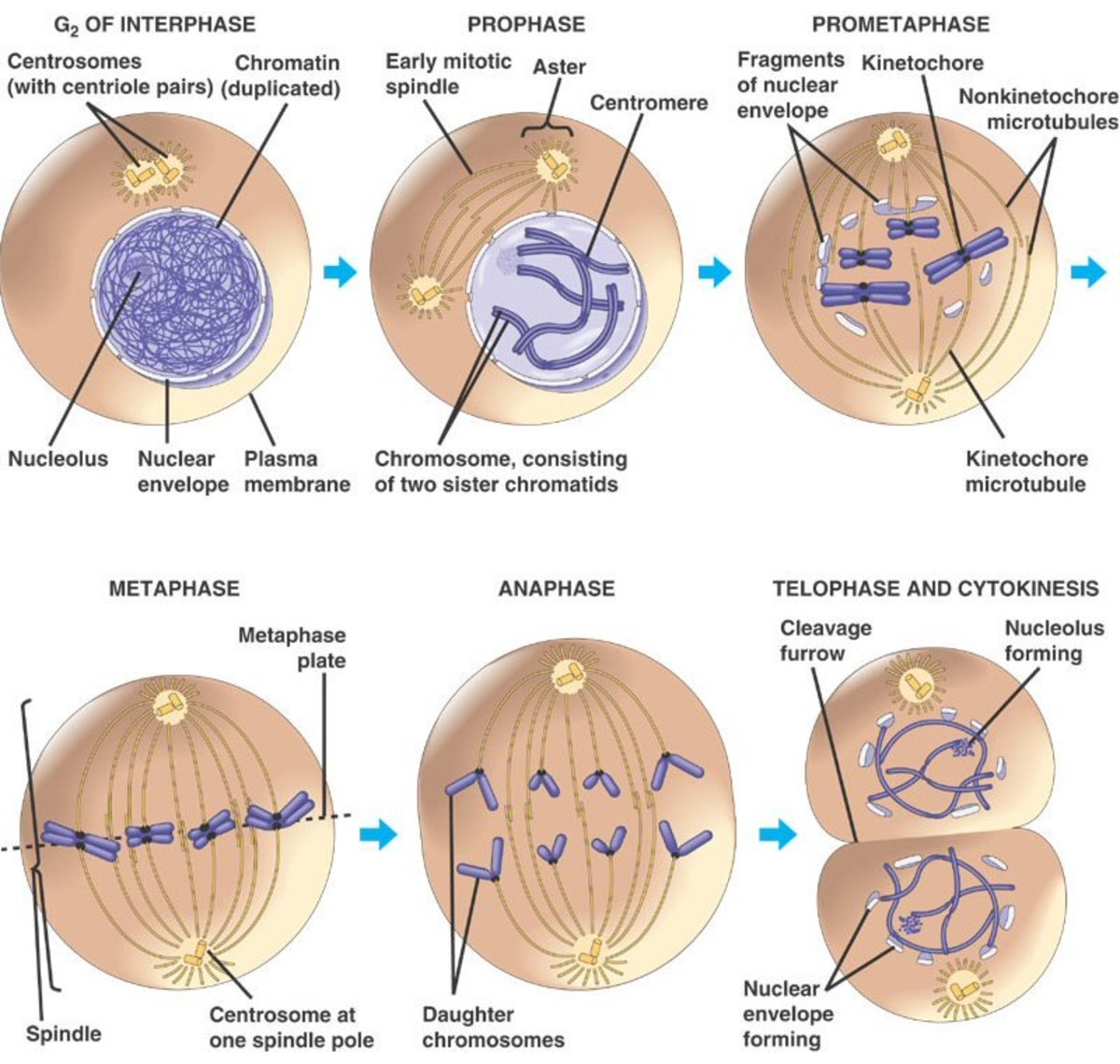
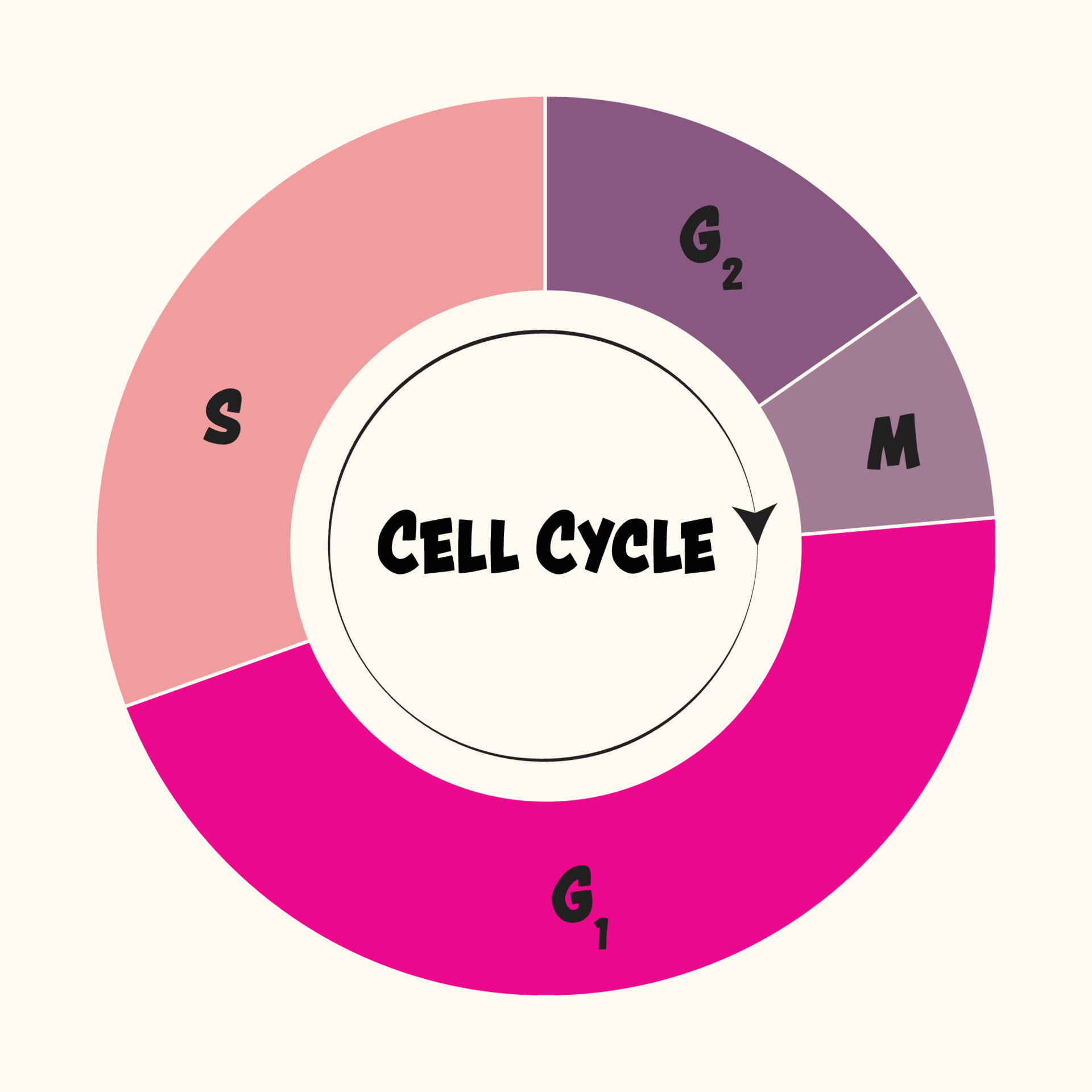
Drawing Of The Cell Cycle
Drawing Of The Cell Cycle - G0, g1, s, g2, m. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. Modification of work by mariana ruiz villareal; As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and. Web identify the stages of the cell cycle, by picture and by description of major milestones. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone) cells. Web life cycle of the cell onion cells in different phases of the cell cycle.growth in an 'organism' is carefully controlled by regulating the cell cycle. Web the most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. Web multiple checkpoints keep track of the cell cycle’s entire process to prevent mistakes in growth and dna synthesis. Figure 5 shows approximately how long a cell spends in each stage of the cell cycle: Phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and makes a copy of its dna: The cell is accumulating the building blocks of chromosomal dna and the associated proteins, as well as accumulating enough energy reserves to complete. During interphase, g 1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the s phase involves dna replication and the replication of the centrosome, and g 2 involves further growth and protein synthesis. In eukaryotic cells, or cells with a nucleus,. Web what is cell cycle? Mitosis and interphase.mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter. The mitotic phase follows interphase. This entire process where with the help of one single parent cell a new cell population grows and develops is known as the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is a set of steps cells go through to grow, replicate, divide, and start the process again. Web phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is a series of events that cells go through to grow, replicate their dna, and divide.this process is vital for the growth, development, repair, and maintenance of living organisms. The cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. At some point, so all of that is interphase. Web the cell. Web the cell is now preparing for the final stage in the cell cycle, cytokinesis. The mitotic phase follows interphase. Phase of the cell cycle where the cell separates its dna into two sets and divides, forming two new cells: Figure 5 shows approximately how long a cell spends in each stage of the cell cycle: The cell is accumulating. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Remember, mitosis is the process of cell division, but it’s just a portion of the full cell cycle. Web the cell is now preparing for the final stage in the cell cycle, cytokinesis. Phase of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is a set of steps cells go through to grow, replicate, divide, and start the process again. Cell cycle in deinococcus radiodurans. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: The series of growth and development steps a cell undergoes between its formation and reproduction: In this way, the cell. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and. Web the interphase part of the life cycle of a cell. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through. Web the most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. In this way, the cell avoids the formation of cancer. At some point, so all of that is interphase. Web what is cell cycle? The series of. Modification of work by roy van heesbeen. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through g0. During interphase, g 1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the s phase involves dna replication and the replication of the centrosome, and. Let's draw a timeline for a cell. Web figure 6.3 a cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. And as we'll see, interphase is where a cell spends most of its life. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. From g0,. Phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and makes a copy of its dna: The series of growth and development steps a cell undergoes between its formation and reproduction: Remember, mitosis is the process of cell division, but it’s just a portion of the full cell cycle. So i'm gonna make it like a cycle so it's gonna. The video quality is not the greatest but if you follow along i highlight some key features fo. From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. It describes the series of events seen when the cell splits into two. Web g 1 phase. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. Figure 5 shows approximately how long a cell spends in each stage of the cell cycle: Modification of work by roy van heesbeen. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is defined as the events that enable cells to proceed from one cell division event to the next. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: This process starts as a cleavage furrow between the cells, making it look like the figure 8. Web understanding the organization of the cell cycle has been a longstanding goal in cell biology. And as we'll see, interphase is where a cell spends most of its life. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. During interphase, g 1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the s phase involves dna replication and the replication of the centrosome, and g 2 involves further growth and protein synthesis. So let's say this is a new cell and it will go through interphase. From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. J wiggers has provided many health care students over the past 100 years with a unique tool to understand the cardiac cycle. It describes the series of events seen when the cell splits into two. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone) cells. G0, g1, s, g2, m.The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
The Cell Cycle Wonders of Life Science
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Phases of the cell cycle Battista Illustration
The Cell Cycle Interphase & Mitosis ALevel Biology Revision Notes
Phases of Cell cycle Online Biology Notes
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
Phases of the cell cycle 6894530 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The First Stage Of Interphase Is Called The G 1 Phase, Or First Gap, Because Little Change Is Visible.
Web The Complete Cell Cycle.
Cell Cycle In Deinococcus Radiodurans.
For Instance, It Might Conduct Signals As A Neuron (Like The One In The Drawing Below) Or Store Carbohydrates As A.
Related Post: